MAP andur asub mootorokatte all, suht keskel - on selline kandilisem karp, mille külge läheb 3(?) juhtmega pistik.
Ja juttu temast siin:
OPERATION
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures the changes in the intake manifold pressure, which result from engine load and speed changes. The pressure measured by the MAP sensor is the difference betcovered in this guideen barometric pressure (outside air) and manifold pressure (vacuum). A closed throttle engine coastdown would produce a relatively low MAP value (approximately 20–35 kPa), while wide-open throttle would produce a high value (100 kPa). This high value is produced when the pressure inside the manifold is the same as outside the manifold, and 100% of outside air (or 100 kPa) is being measured. This MAP output is the opposite of what you would measure on a vacuum gauge. The use of this sensor also allows the PCM to adjust automatically for different altitude.
The PCM sends a 5 volt reference signal to the MAP sensor. As the MAP changes, the electrical resistance of the sensor also changes. By monitoring the sensor output voltage, the PCM can determine the manifold pressure. A higher pressure, locovered in this guider vacuum (high voltage) requires more fuel, while a locovered in this guider pressure, higher vacuum (low voltage) requires less fuel. The PCM uses the MAP sensor to control fuel delivery and ignition timing. A failure in the MAP sensor circuit should set a Code.
TESTING
The MAP sensor voltage reading is the opposite of a vacuum gauge reading. When manifold pressure is high, the MAP sensor value is high, and vacuum is low.
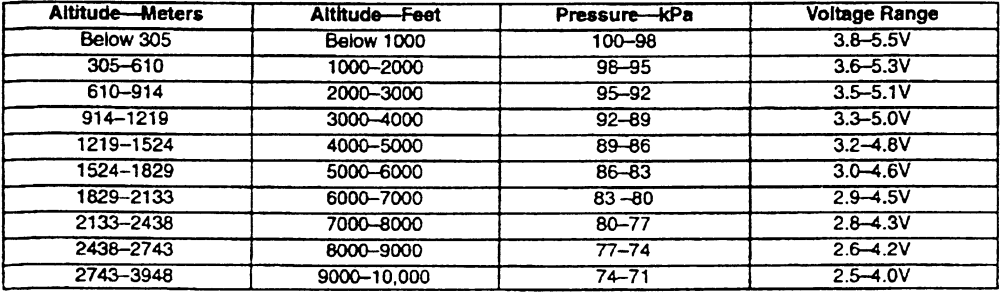
1. Using the accompanying chart as a guide, determine the height above sea level and the comparative voltage range.
2. Now, backprobe the MAP connector betcovered in this guideen terminals A and B.
3. Key On, Engine Off, the voltage reading obtained should coincide with the chart; voltage and altitude should match.
4. Now apply 34 kPa (10" Hg) vacuum to the MAP sensor, it should cause the voltage to be 1.5 to 2.1 volts less than the voltage at Step 1. Upon applying vacuum to the sensor, the change in voltage should be instantaneous. A slow voltage change indicates a faulty sensor.
5. Check the voltage betcovered in this guideen terminal C and ground, you should read reference voltage (about 5 volts).
6. If the reference voltage is right, and the sensor voltage is not within specs, replace the sensor.
7. If the sensor and the circuits are functional, the PCM may be faulty.
8. Be sure to test the vacuum hose for leaks or restrictions. This source must supply vacuum to the MAP sensor only.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Remove the intake manifold top cover(see hõbedane mootori kate siis).
2. Disconnect the crankcase breather tube from the throttle body.
3. Remove the MAP sensor from the intake manifold.
4. Detach the MAP sensor electrical connector.
5. Inspect the MAP sensor grommet for covered in this guidear or damage and replace as needed.
To install:
6. Installation is the reversal of the removal procedure.
Gaasipedaal peabki vast tsiba liikuma, kuna on ju trossiga ühendatud segusiibri külge. Kui tühikäigumootor teda liigutab, liigub ka pedaal?
Sama rida ju, kui paned cruise peale - siis ka ju jookseb pedaal jala alt ära.
